No credit check credit cards can help people with poor credit establish a good credit history. In most cases, there is a credit card for nearly everyone plus you can be approved within minutes.
When your credit is really bad, no credit check credit cards can help you bounce back. But you must use credit responsibly. Credit cards are simple, easy to use tools to build or rebuild credit history when properly managed.
No-Credit Check Credit Cards
It will likely take up to 6 months to establish your credit history with on-time monthly payments.
1. OpenSky® Secured Visa® Credit Card
Highlights
- No credit check necessary to apply. OpenSky believes in giving an opportunity to everyone.
- The refundable* deposit you provide becomes your credit line limit on your Visa card. Choose it yourself, from as low as $200.
- Build credit quickly. OpenSky reports to all 3 major credit bureaus.
- 99% of our customers who started without a credit score earned a credit score record with the credit bureaus in as little as 6 months.
- View our Cardholder Agreement located at the bottom of the application page for details of the card.
2. OpenSky® Plus Secured Visa® Credit Card
Highlights
- $300 minimum refundable security deposit. Click “Apply Now” to see additional terms and conditions.
- No annual fee.
- No credit check to apply. Zero credit risk to apply!
- Looking to build or rebuild your credit? 2/3 of cardholders receive a 48+ point improvement after making 3 on-time payments
- Extend your $300 credit line by getting considered for an unsecured credit line increase after 6 months – no additional deposit required!
- Build your credit history across 3 major credit reporting agencies: Experian, Equifax, and Transunion
- Fund your security deposit over 60 days with the option to make partial payments
3. The Current Build Card
Highlights
- You must open a Current account before applying for the Build Card. Funds transferred into the Current account become your security deposit.
- Build credit with every swipe.
- Get paid up to 2 days faster.
- Earn points on swipes for cash back.
- No credit checks or history required.
How no credit check credit cards work
When you apply for a credit card, most credit card issuers will check your credit reports. But with no credit check credit cards, the credit card issuer will pre-qualify you prior to running a hard inquiry credit check.
When a credit card company pre-qualifies you, they make a soft-inquiry on your credit files. Soft inquiries don’t take points off your credit scores.
To get a no credit check credit card, you’re usually only required to:
- Have a source of income
- Have a checking account
- Be at least 21 years old or 18 years old with either a parent's permission or a verifiable source of income
- Have a Social Security number
What to watch out for with no credit check credit cards
There are a few downsides to no credit check credit cards that you may want to consider.
High interest rates: You can expect no credit check credit cards to have higher interest rates.
That’s because credit card companies that deal with subprime credit often charge high APRs to hedge the risks that come with bad credit.
High fees: Expect several fees to come with no credit check credit cards. There may be an application, setup, and maintenance fees.
No rewards or benefits: Unlike many of the top travel or cash back cards, these cards usually don’t come with any perks.
How to manage your new credit accounts
Pay your bill in full each month to avoid owing interest. Interest is the is the price you’ll pay for borrowing money. If you carry a balance, you’ll pay interest…it’s that simple.
Credit card companies generally give you at least a 21-day grace period between the purchase date and when the payment is due. If you pay off your balance in full, you won’t be charged interest on new purchases made during this interval.
Here is an example of not paying your balance in full:
Let’s say you have a new card with a 15 percent APR (annual percentage rate). At the end of the first month, your balance is $300 and your minimum payment is $25.
Once you pay the $25 minimum payment, your balance is now $275. The $275 balance will begin accruing interest at 15 percent until you make the next monthly payment.
When you carry a balance, your balance just keeps getting bigger because you begin paying interest on a balance that includes the previously accrued interest.
Once your balance continues to grow, especially if you only pay the minimum due each month, you end up paying much more than the original amount you put on your credit card.
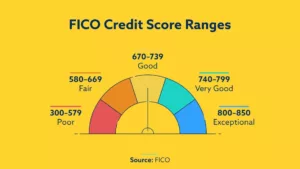
Habits to improve credit scores
There are few simple habits that will improve your credit scores.
Pay your bills on time: This is probably the most important factor. One late or missed monthly payment can stay on your credit reports for up to seven years. We suggest setting up automatic payments so you never miss a due date.
Keep low credit card balances: A major part of your credit score is the amount of available credit you’re using. Never max out your credit card. Do your best to keep your balances low. In fact, using ten percent or less of your available credit will tremendously help your scores.
Keep old accounts open. Keeping your oldest accounts open and remember to use them from time-to-time so the accounts remain active.
Monitor your credit reports: Sign up for a free credit monitoring service to keep an eye for identity theft or fraud.
Get familiar with credit card terms
As a credit card holder, it's important to understand credit card terms and conditions. Taking the time to understand how your finances work helps you make more informed decisions, avoid unnecessary fees and charges, as well as protect yourself from fraud and theft.
Here are some common credit card terms:
- Annual Percentage Rate (APR): The annual interest rate charged on outstanding credit card balances.
- Balance Transfer: A process of transferring outstanding balances from one credit card to another credit card.
- Credit Limit: The maximum amount of credit extended by the credit card issuer to the cardholder.
- Grace Period: The period during which no interest is charged on new purchases made on the credit card.
- Minimum Payment: The minimum amount that a cardholder must pay each month to avoid late fees and penalties.
- Rewards Program: A program offered by credit card issuers that allows cardholders to earn rewards or points for purchases made on their credit card.
- Annual Fee: A fee charged by the credit card issuer for the privilege of using the credit card.
- Cash Advance: A cash loan obtained from the credit card issuer, usually with high fees and interest rates.
- Foreign Transaction Fee: A fee charged for using a credit card outside of the cardholder's country.
- Late Payment Fee: A fee charged for making a late payment on the credit card.